1. Acne

- Effective acne treatments are available, but acne can be persistent. One has to consult a dermatologist with a good follow up to get rid of such symptoms.
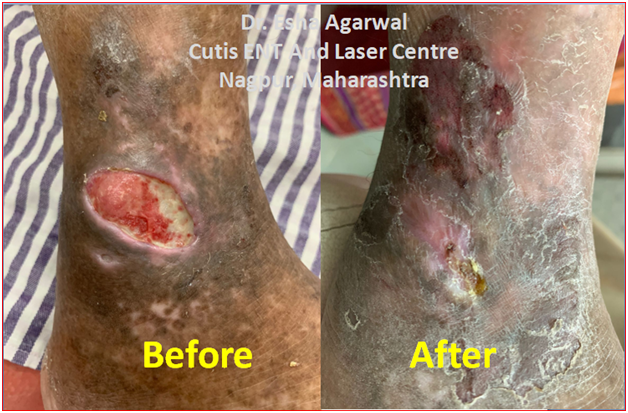
- Once Acne Scars sets in, it can be very well treated with Laser resurfacing/microneedling RF of face.
- Contact us to know about the latest and best treatment for such symptoms.
2. Melasma
- Life style alterations to avoid sun light.
- Proper balanced diet.
- Avoiding Stress.
- Avoiding harmful cosmetics and facials.
- Sunscreens
- Skin lightening creams
- Mild peeling agents
- Use of mild steroid creams
- The above drugs may be used in combination-called Kligman’s formula.
- Laser Treatment
Continuous maintenance treatment is necessary to prevent recurrence. And with each recurrence, pigmentation penetrates deeper, and becomes more and more difficult to treat.
3. Keloids/Hypertrophic Scars
- Intralesional steroid injections
- Cryotherapy
- Laser treatment
Hypertrophic scars
Keloids
4. Chemical Peeling
A chemical peel is a technique used to improve the appearance of the skin on the face, neck, hands or full body. A chemical peel uses a solution which consists of fruit derived acids in low concentrations with balanced pH to remove layers of skin, revealing the more youthful skin. Chemical peels can reduce or improve fine lines and wrinkles, acne, scars, uneven skin coloring and other skin imperfections. The new, regenerated skin is usually smoother and less wrinkled than the old skin.
Chemical peels are most commonly performed on your face, neck or hands. They can help reduce or improve:
- Fine lines under your eyes or around your mouth and wrinkling by sun damage, aging and hereditary factors.
- Certain types of acne.
- Mild scarring.
- Sun spots, age spots, liver spots, freckles, uneven skin coloring.
- Precancerous scaly spots called actinic keratosis.
- Rough skin, scaly patches, dull complexion.
- Dark patches (melasma) due to pregnancy or taking birth control pills.
5. PRP
INDICATIONS OF PRP
Hair Loss

Skin Rejuvenation

6. PRF
7. Botox
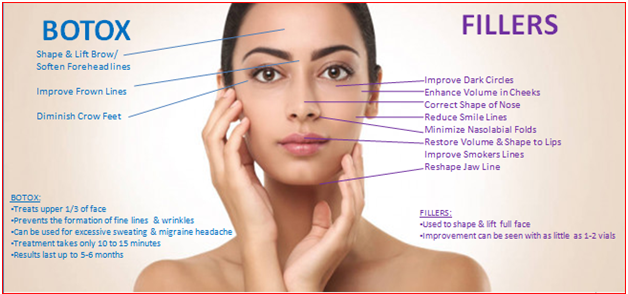
8. Dermal Fillers
- Facial lines (wrinkles, folds)
- Lip enhancement
- Facial deformities
- Depressed scars
- Breast, buttock augmentation
- Periocular melanoses, sunken eyes
- Dermatological diseases-angular cheilitis, scleroderma, AIDS lipoatrophy
- Earlobe plumping, earring ptosis
9. Dark Circle
- lack of sleep or poor sleeping habits
- allergies, including hay fever
- hyperpigmentation, which happens when the body produces more melanin
- reduced levels of fatty tissue around the eyes
- thinning skin under the eyes
- anemia from iron deficiency
- overexposure to sunlight
- frequent rubbing of the eyes
- aging
- smoking
- thyroid disease
- dehydration
- dermatitis
- Adequate sleep
- Smoking cessation
- Sleep with extra pillows to elevate the head and reduce eyelid swelling
- Massage temporary swelling while applying a cold compress
- Cold compresses also minimise the appearance of prominent blood vessels
- Cosmetic camouflage
- Protection from sun exposure using sunglasses
- Topical agents; however dermal pigmentation responds poorly, and eyelids are sensitive so the stronger products may irritate (see melasma)
- Chemical peels to reduce fine lines and surface pigmentation
- Laser treatments.
- Dermal Fillers is a solution to such problems