Skin Conditions
Pregnancy Dermatoses
- The dermatoses of pregnancy are a heterogeneous group of pruritic/itchy inflammatory dermatoses that occur exclusively during pregnancy and/or in the immediate postpartum period. These include the following conditions:
- Pemphigoid gestationis
- Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy (pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy [PUPPP])
- Atopic eruption of pregnancy (eczema in pregnancy, prurigo of pregnancy, pruritic folliculitis of pregnancy)
- Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
- Skin Care Tips to follow during pregnancy that every mother to be should keep in mind
- Drink Plenty of Water
- Sleep for atleast 8-10 hours a day
- Take a balanced diet
- Sun Protection
- Avoid Stress
- Regular Light Exercise
- Avoid Harsh Soaps & Face Wash
- Use of Fragrance free moisturizers liberally
Paediatric Dermatoses
- Use of Gentle Skin Cleansers
- Liberal use of Moisturizers
- Sun Protection
- Everyone loves the idea of their baby smelling great, but products with fragrances are often associated with allergies, dermatitis, respiratory problems, and other side effects. To avoid any skin complications, ensure the moisturizer you choose is fragrance-free.
- Parabens are widely used as preservatives in body washes, shampoos, facial cleansers, and deodorants. They can also cause irritations and allergies in young children, so it’s best to avoid these as well.
- Formaldehyde-releasing preservatives (FRPs) are sometimes used to help prevent bacterial growth, but this chemical can also lead to allergies and irritation and may even be harmful to the immune system. It’s a good idea to avoid any cleansers, body washes, conditioners, or shampoos with this ingredient.
- Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS)/Sodium laureth sulfate (SLES). Approximately over 90 percent of shampoos and body washes contain sulfates.6 SLSs can irritate the eyes, skin. So. It is best to avoid such products for your children.
Geriatric Dermatoses
It includes the spectrum of skin conditions in elderly. As you age, your skin naturally ages along with you. The production of collagen and elastin slows down, which causes your skin to lose some elasticity. Skin also becomes thinner and more fragile; glands lose their ability to effectively moisturize the skin; and it’s therefore common for older adults to have dry skin. Besides these natural effects of aging, the environment can have a compounding effect, including when a person gets too much sun or has been exposed to harsh weather conditions. A person’s ethnicity and heredity are also factors in how his or her skin ages. Since skin of the elderly population is going through a lot of changes from both an intrinsic and extrinsic point of view. The pathophysiology of geriatric skin disorders and their specific management, slightly from an adult population.
Here are some handy tips for skin care in elderly
- Wash Gently
- Sun Protection
- Liberal use of Moisturizers
- Balanced Diet
- Drink Plenty of Water
- Avoid Smoking
If still it is not working. You can contact me for an individualized skin care plan.
Blistering Disorders
- Pemphigus Vulgaris – It is the most common type of blistering disorder. It occurs mostly in the age group of 40 – 50 years and affects both genders.
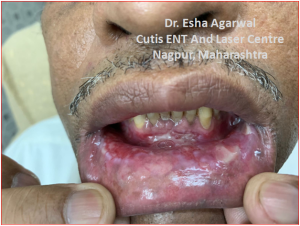
- Bullous Pemphigoid – It is usually an acquired autoimmune blistering disease of the elderly.
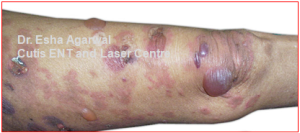
Moles
Treatment of Moles
Food Allergy
- Itching of the mouth can be an immediate symptom with onset within seconds of coming in contact with the allergic food.
- Swelling of the face may happen on eating the food. The swelling mostly affects the lips, cheeks and eyelids. This is also known as Angioedema.
- Swelling of the tongue, lips and throat can come on after a few minutes and can be quite dramatic. This can have a rapid onset within minutes. Also known as “Oral Allergy Syndrome”
- Abdominal pain (stomach cramps) and vomiting may also occur if the food to which there is an allergy is swallowed. This is a protective response of body, which tries to throw the allergic material out of the body.
- Diarrhea is a symptom that would happen each time after eating an allergy food.
- A widespread rash can also occur with a food allergy within half an hour of eating the food.The rash is itchy with wheals/edema.
Identifying the Allergen (Food)
- Maintaining a diary – Try keeping a food and symptom diary. Write down everything that you eat and drink and how good or bad your skin problem is. Grade your skin problem according to your symptoms on a scale 0f 1-10. You may need to keep this dairy for a few months.
- Skin Prick Testing
- Blood Test
Proper followup and study is needed to identify that patient has food allergy.