Throat
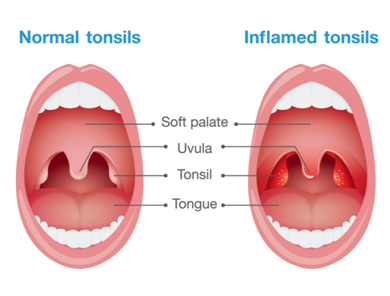
Tonsil
The tonsils (palatine tonsils) are a pair of soft tissue masses located at the rear of the throat. They are normally present in children below 7- 8 years of age and are responsible for immunity and fighting infections in young children. They slowly regress in size as the child grows. In some individuals they may be enlarged even in adulthood.
The common conditions are :-
- Acute tonsillitis: A bacteria or virus infects the tonsils, causing swelling and a sore throat. The tonsil may develop a gray or white coating (exudate).
- Chronic tonsillitis: Persistent infection of the tonsils, sometimes as a result of repeated episodes of acute tonsillitis.
- Peritonsillar abscess: An infection creates a pocket of pus next to the tonsil, pushing it toward the opposite side. Peritonsillar abscesses must be drained urgently.
- Tonsilloliths (tonsil stones): Tonsil stones, or Tonsilloliths, are formed when trapped debris hardens, or calcifies.
Treatment
Medical and Surgical
Surgical – Latest Technology in Surgical option is Coblation, more recent than Laser procedure.
COBLATION technology combines radiofrequency energy and saline to create a plasma field. The plasma field remains at a relatively low temperature as it precisely ablates the targeted tonsil tissue. The COBLATION plasma field removes target tissue while minimizing damage to surrounding areas. This helps in faster and relatively painfree recovery.
Contact your Specialist to have a diagnosis of your condition and specific treatment
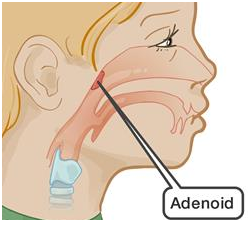
Adenoid
It is a mass of lymphatic tissue between the back of the nose and the throat.
When it is enlarged it can lead to many symptoms as followss :-
- chronic mouth breathing
- snoring,
- sleep disturbance,
- halitosis,
- recurrent ear infections
- hearing loss
- hyponasal voice change
- Diagnosis
- Nasal Endoscopy
- X ray
- CT PNS
Treatment
Medical and Surgical.
Surgical – Endoscopic Adenoidectomy with Coblation- i.e. the procedure is done under visual control rather than as a blind procedure done earlier. It is done through natural holes ( Nose/Mouth) without an scars or stitches.
Latest Technology in Surgical option is Coblation, more recent than Laser procedure.
COBLATION technology combines radiofrequency energy and saline to create a plasma field. The plasma field remains at a relatively low temperature as it precisely ablates the targeted tonsil tissue. The COBLATION plasma field removes target tissue while minimizing damage to surrounding areas. This helps in faster and relatively painfree recovery.
Contact your Specialist to have a diagnosis of your condition and specific treatment
Voice Change
It is a very common symptom rather an actual condition requiring treatment.
Voice change can occur during a common cold, due to post nasal drip (discharge from the back of the nose irritates the throat and the voice box). The throat pain and change in voice subsides with treatment for the common cold.
Laryngitis and reflux disease can also present as voice change, along with excessive burping, burning in the chest region. This can be treated with antacids, avoiding tea, coffee and carbonated drinks, and drinking water frequently.
In singers / teachers/ hawkers / eloquitors voice change is due to voice abuse, i.e excessive use of the voice in a high pitch makes the voice box swollen and small masses – nodules/polyps, develop on the vocal cords. These are called screamer/singers nodules. These nodules are harmless and NOT cancerous.
Rarely voice change, in smokers or tobacco chewers can be cancer of the voice box.
Diagnosis
Voice change is investigated by examination of the voice box by video laryngoscopy.
An endoscope(Hopkin’s Rod/ Flexible Scope) connected to a camera is used in this procedure. Local anaesthetic spray is used to numb the back of the throat to prevent vomiting sensation and facilitate procedure. The endoscope is just kept at the back of the tongue and does not enter the voice box. The procedure takes only 1-2 minutes and is not painful.
Treatment
Contact your doctor to have a diagnosis and the treatment of the condition can be done accordingly as Medical/ Surgical.
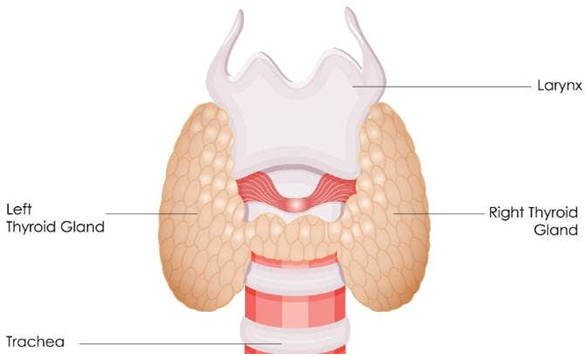
Thyroid
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland that lies low on the front of the neck. It lies below the Adam’s apple, along the front of the windpipe. The thyroid has two side lobes, connected by a bridge (isthmus) in the middle. Thyroid is an endocrine gland that secretes hormones into your bloodstream. It provides a vital function by regulating your metabolism.
There can be many Medical/ Surgical conditions relating to this gland.
1. Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
Hypothyroidism is a health condition characterized by unusually low hormone production.
It is when your thyroid gland becomes underactive and cannot produce enough hormones to regulate your metabolism.
If your thyroid can’t secrete enough hormones into your bloodstream, your body’s metabolism slows down rapidly.
2. Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
Hyperthyroidism is a health condition that occurs when your thyroid gland becomes overactive and produces more thyroid hormones than you need.
When you have hyperthyroidism your metabolism speeds up, making your body work harder and faster.
It is a common condition affecting more women than men.
3. Goitre (enlarged gland)
It Is a condition when the gland is enlarged in size, may be one side or both sides leading to unsightly appearance.
It can be due to benign(non-cancerous) or malignant ( cancerous) conditions.
Treatment
Contact your doctor to have a diagnosis and the treatment of the condition can be done accordingly as Medical/ Surgical.